A Reinforcement Learning approach to the location of the non
4.9 (186) · $ 23.99 · In stock


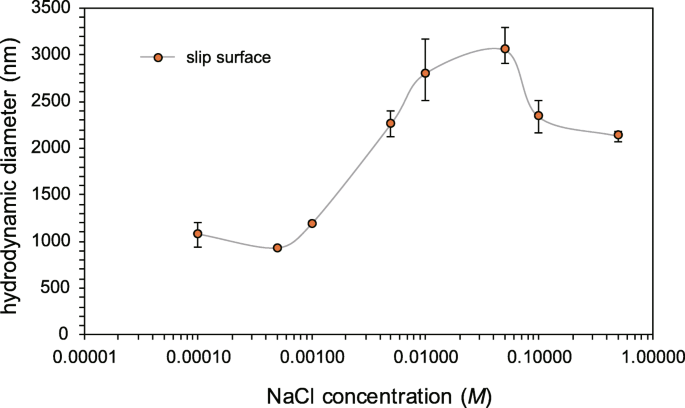
Generating Slip Surfaces Using the Logistic Function Integral, International Journal of Geomechanics

Generative Learning Plan Recommendation for Employees: A Performance-aware Reinforcement Learning Approach

Forests, Free Full-Text

Forests, Free Full-Text
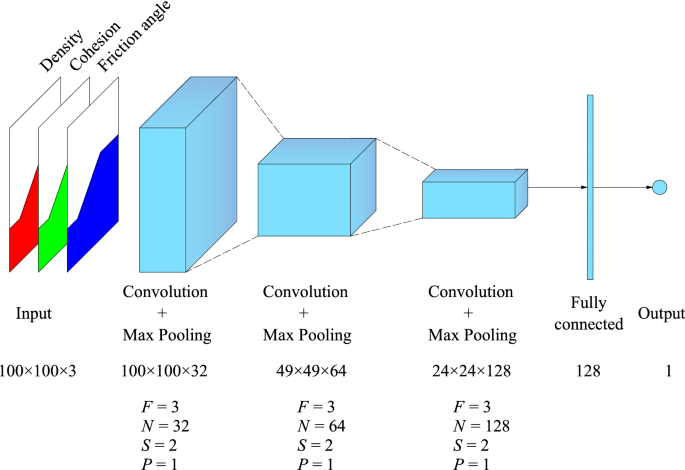
Convolutional neural networks prediction of the factor of safety of random layered slopes by the strength reduction method

A Reinforcement Learning approach to the location of the non-circular critical slip surface of slopes - ScienceDirect

Deep Reinforcement Learning for Mineral Prospectivity Mapping

Reliability Analyses of Soil Slopes with Multiple Spatially Varying Parameters Using Multi-Input Convolutional Neural Networks, International Journal of Geomechanics

LA solutions of stability numbers for b = 60°: (a) d/H = 1.5, (b) d/H =

Forests 14 00808 v3, PDF, Soil Mechanics

Convolutional neural networks prediction of the factor of safety of random layered slopes by the strength reduction method