Chapter 3: The Basics of Classical Mechanics
4.9 (786) · $ 11.50 · In stock

Chapter 3: The Basics of Classical Mechanics
![Classical Mechanics] Compute directly the gravitational force on a unit mass at a point exterior to a homogeneous sphere of matter. : r/PhysicsStudents](https://preview.redd.it/classical-mechanics-compute-directly-the-gravitational-v0-o3isahf2acka1.png?width=833&format=png&auto=webp&s=617560a138f75df57e80cb04b28f336cb03fc98a)
Classical Mechanics] Compute directly the gravitational force on a unit mass at a point exterior to a homogeneous sphere of matter. : r/PhysicsStudents
Classical physics - Wikipedia

Hyeokyoung Lee - The Medium, of Architecture. Gerrit Rietveld, Rietveld schröder house
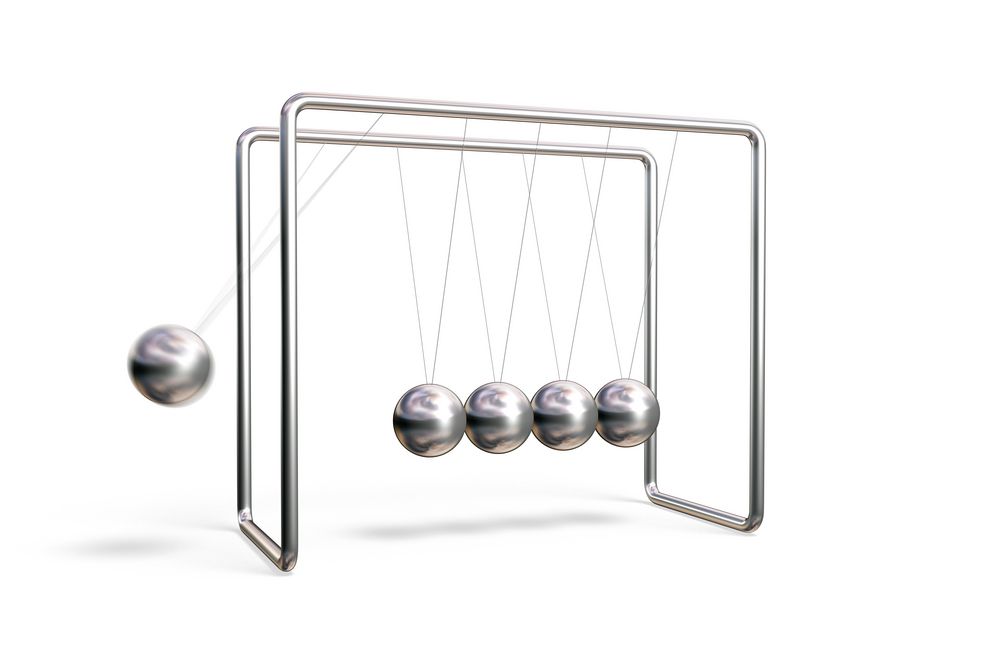
What Is Classical Mechanics?

Table of Contents

SOLUTION: Classical mechanics chapter 3 lecture 3 - Studypool

Classical mechanics

Mechanical Design Handbook, Second Edition
![The classical mechanics of the special theory of [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theclassicalmechanicsofthespecialtheoryofautosaved-201210192631/85/the-classical-mechanics-of-the-special-theory-of-autosaved-3-320.jpg?cb=1670784896)
The classical mechanics of the special theory of [autosaved]

SOLUTION: Classical mechanics chapter 3 lecture 3 - Studypool

solutions-for-chapter-3.pdf - Solutions for Classical Mechanics - Goldstein.H 2ndedition Muthumanimaran V M.Sc. Physics Department of Theoretical

Chapter 3 Force and Newton's laws. Issac Newton (1642 - 1727 ) Galileo Galilei (1564 - 1642 ) Section 3-1 Classical mechanics The approach to the dynamics. - ppt download
Mechanics - Definition & Types (Classical, Quantum & Statistical)







