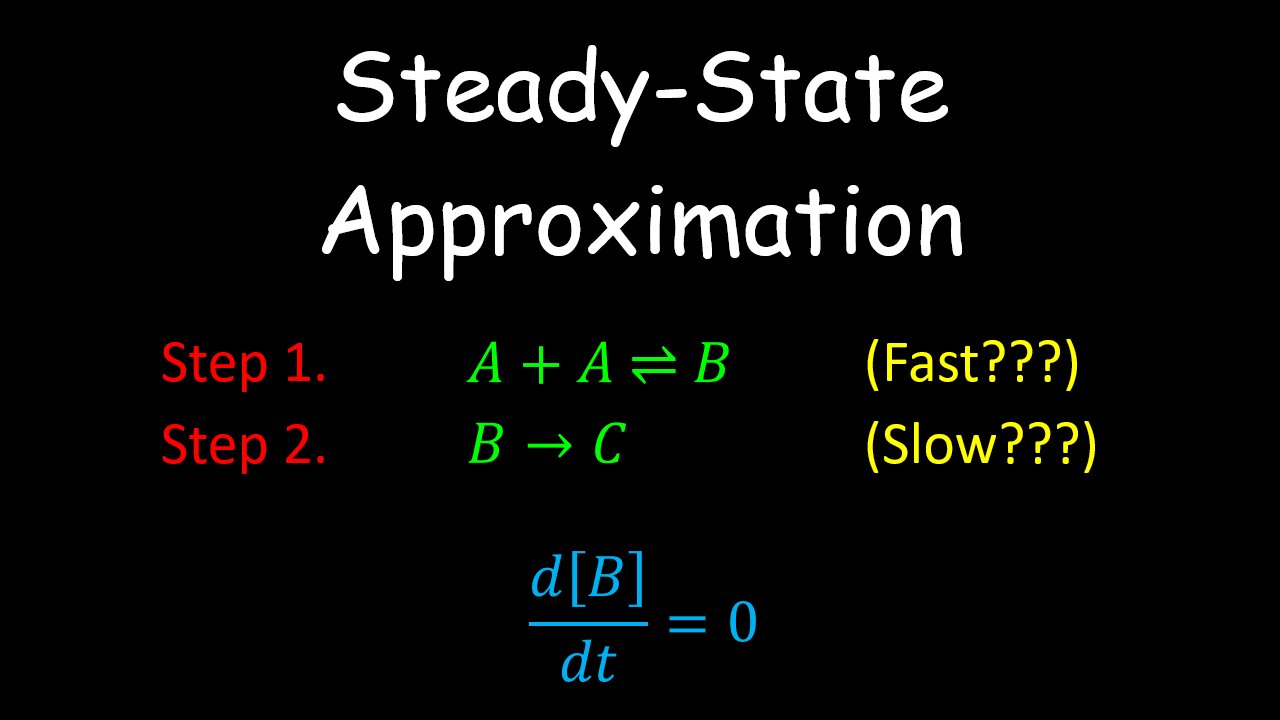
3 Solving for the steady state Notes on Solow Model for Econ 110
4.6 (594) · $ 19.99 · In stock
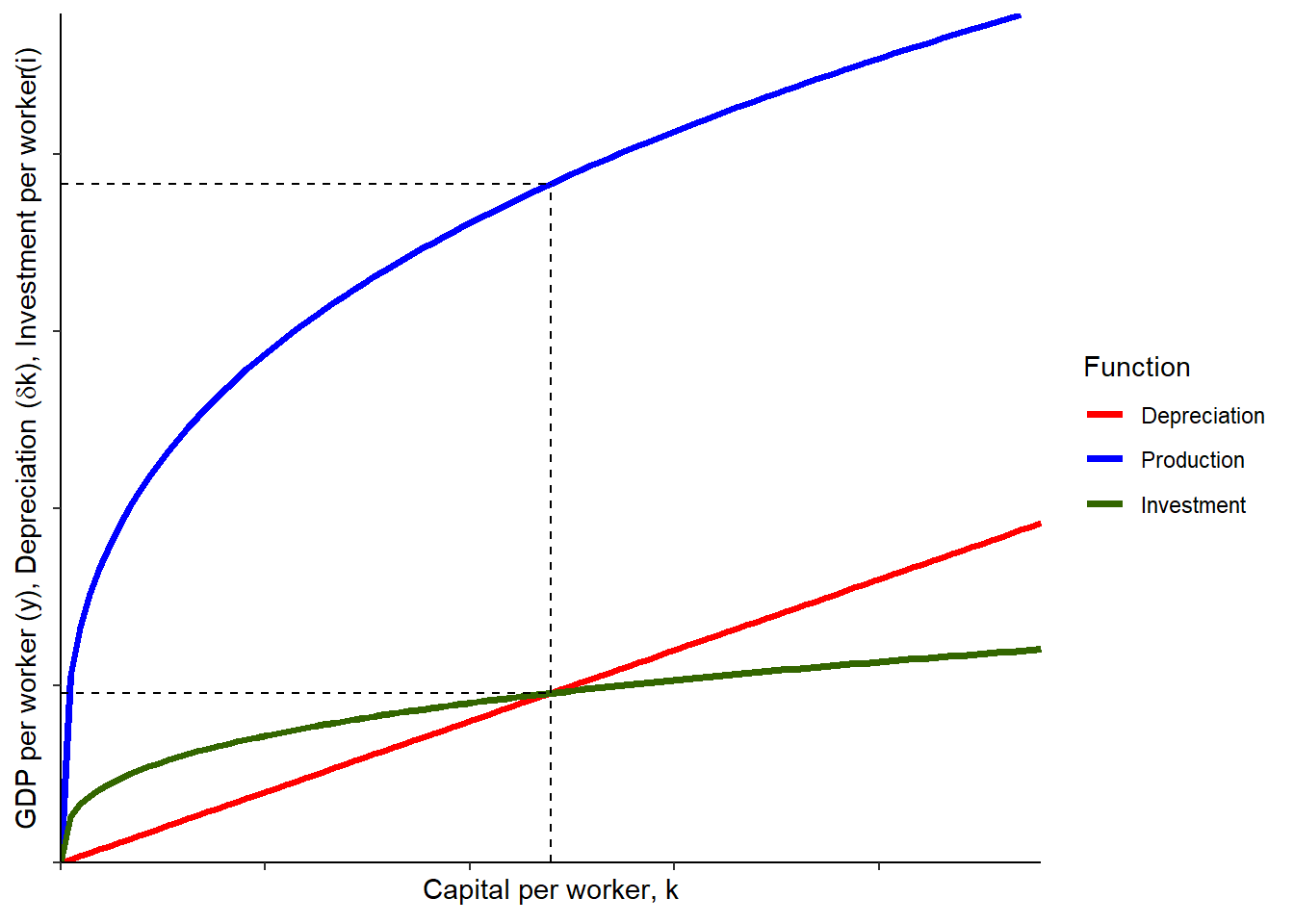
3 Solving for the steady state | Notes on Solow Model for Econ 110

SOLVED: Text: 2. Solow Model with Technological Progress [25

Solow Model, PDF, Economic Growth
![SOLVED: Question 1: Basic Solow Model [20 Points] Assume an economy has the following production function: Y = F(K,L) = 10K^7L^3 Assume that the savings rate is 0.18, the depreciation rate is](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/fee21dd3529543f5b96c6e587eb37a59.jpg)
SOLVED: Question 1: Basic Solow Model [20 Points] Assume an economy has the following production function: Y = F(K,L) = 10K^7L^3 Assume that the savings rate is 0.18, the depreciation rate is

Problem set 4 - lectıre notes - 1 ECON 507 Macroeconomic Theory I Problem Set 4: 1. (Romer 2) A - Studocu

Solow Growth Model Basics - Nicholas J. Sanders
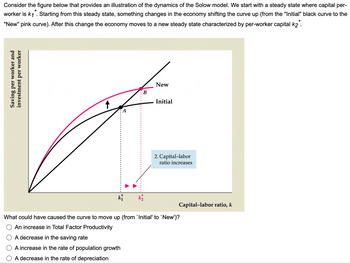
Answered: Consider the figure below that provides…

Macroeconomic dynamics in a finite world based on thermodynamic potential
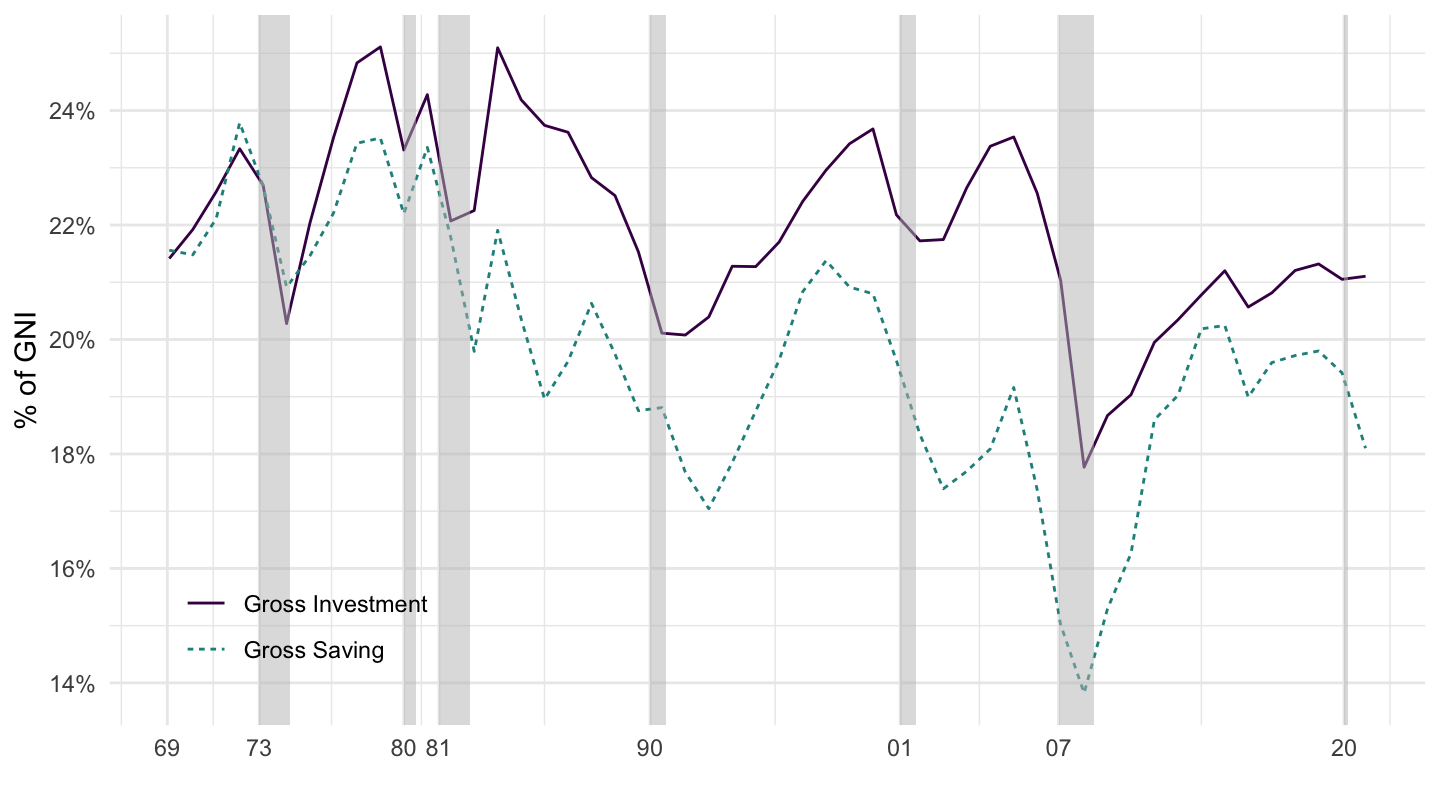
3 Capital Accumulation Intermediate Macroeconomics
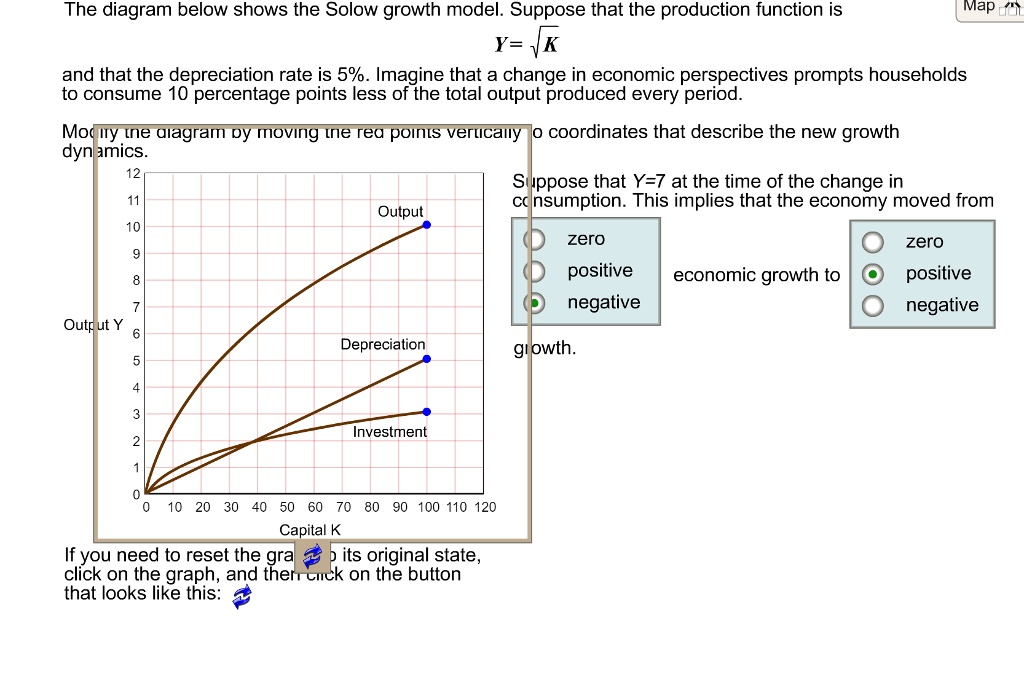
SOLVED: Please fill out the graph for this. The diagram below
econ-w3213-recitation-notes/06 Solow Swan Growth Model.tex at
PDF) A conceptual analysis of economic growth based on the Solow model

Chapter 5 - Solow Model for Growth
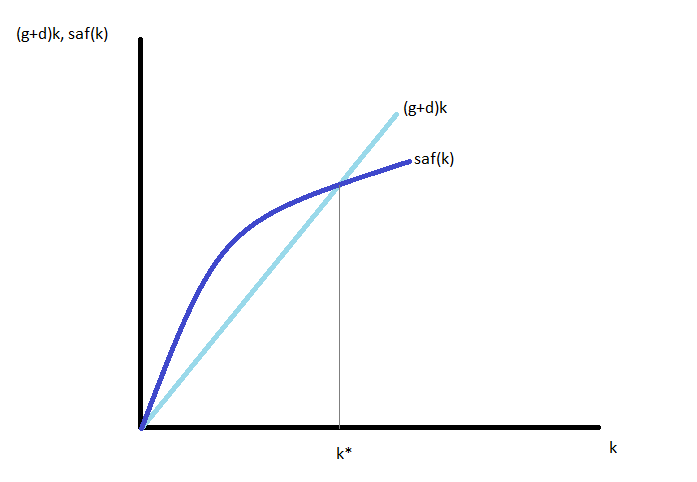
Solow Growth Model - Overview, Assumptions, and How to Solve