Repressive elements co-evolve with splice site sequences at cryptic
5 (607) · $ 27.50 · In stock

A deep exon cryptic splice site promotes aberrant intron retention
Frontiers Splicing in the Diagnosis of Rare Disease: Advances

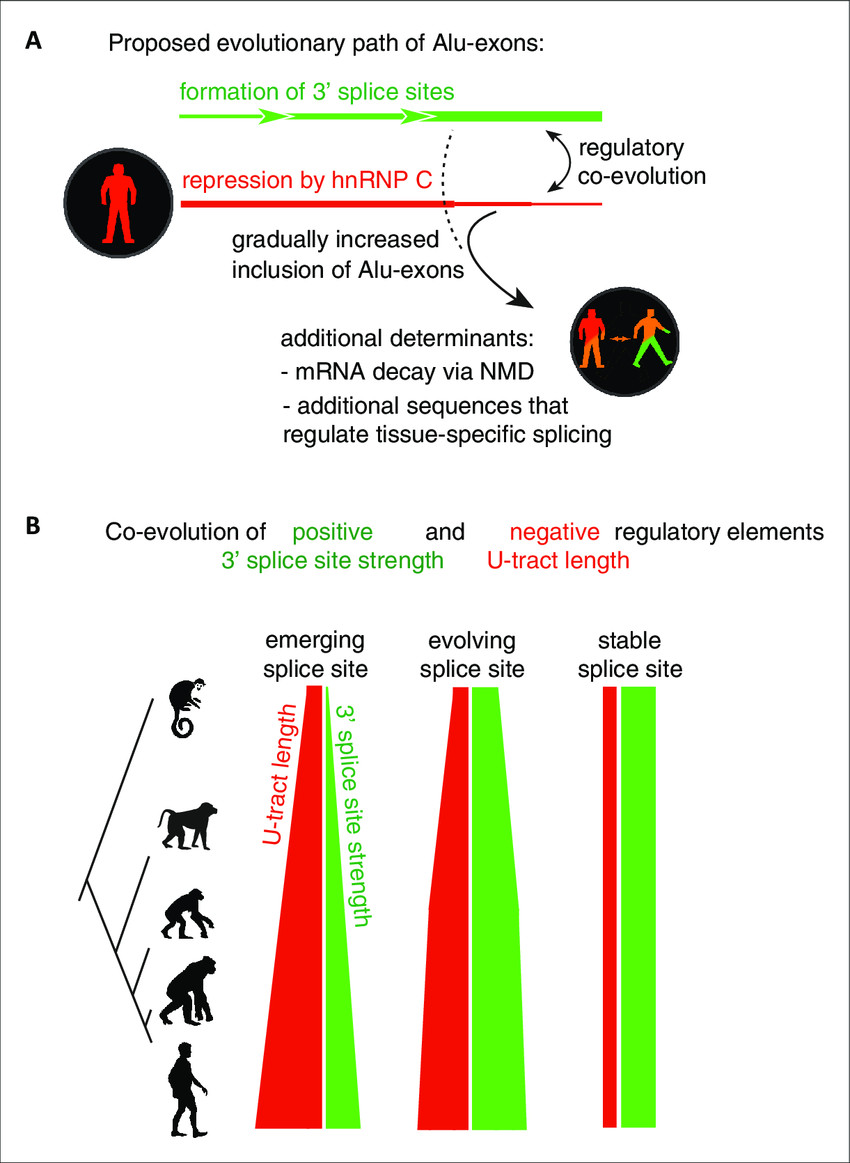
Splicing repression allows the gradual emergence of new Alu-exons in primate evolution. - Abstract - Europe PMC
Alternative splicing as a source of phenotypic diversity
Splicing mutations in human genetic disorders: examples, detection
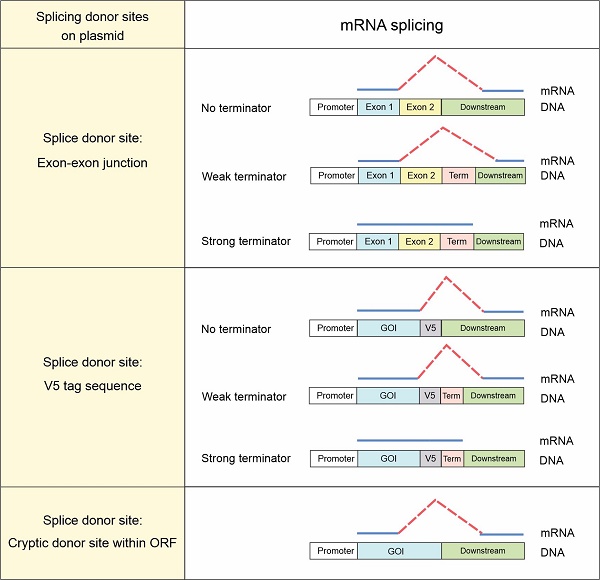
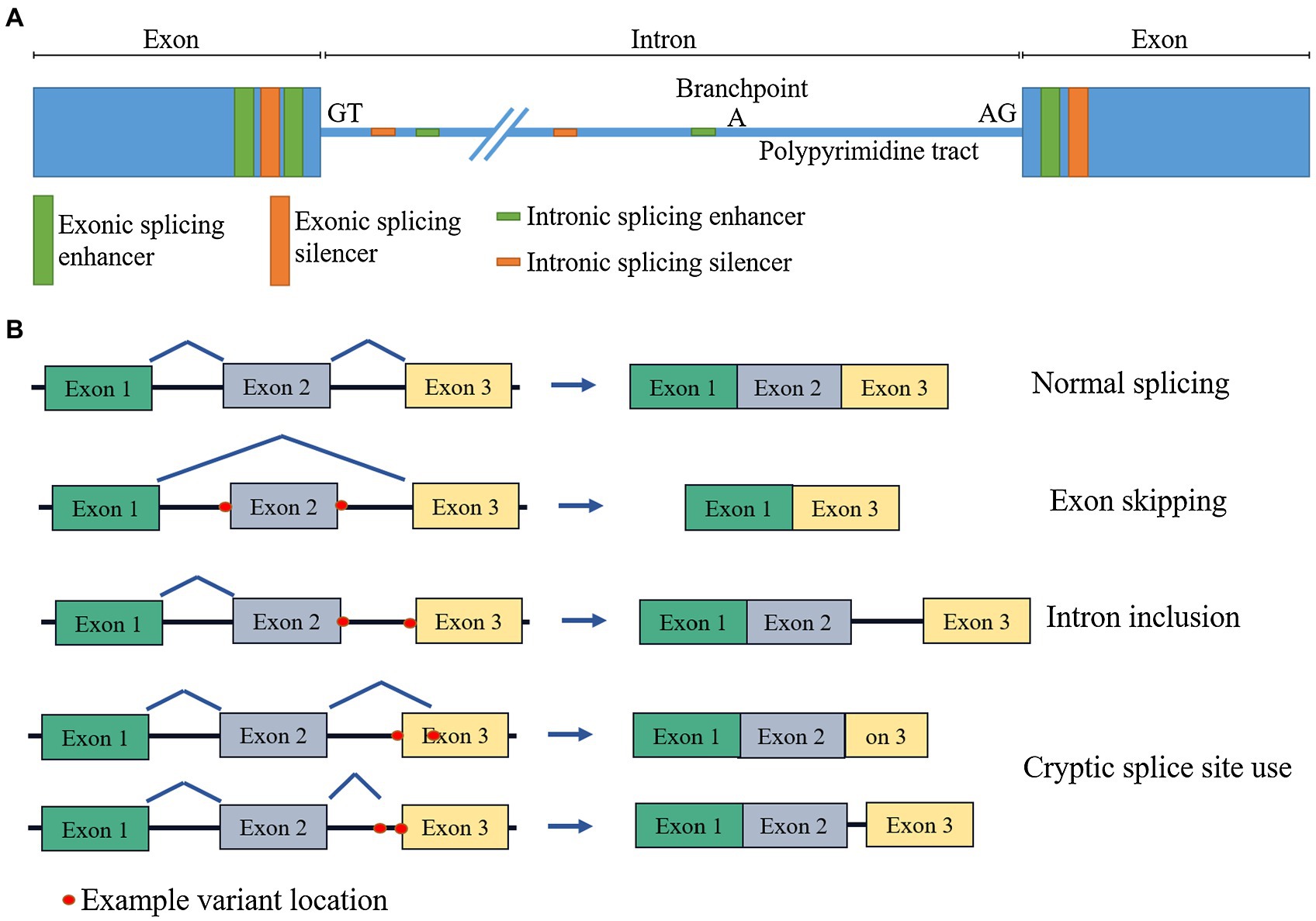
Aberrant splicing events caused by insertion of genes of interest into expression vectors

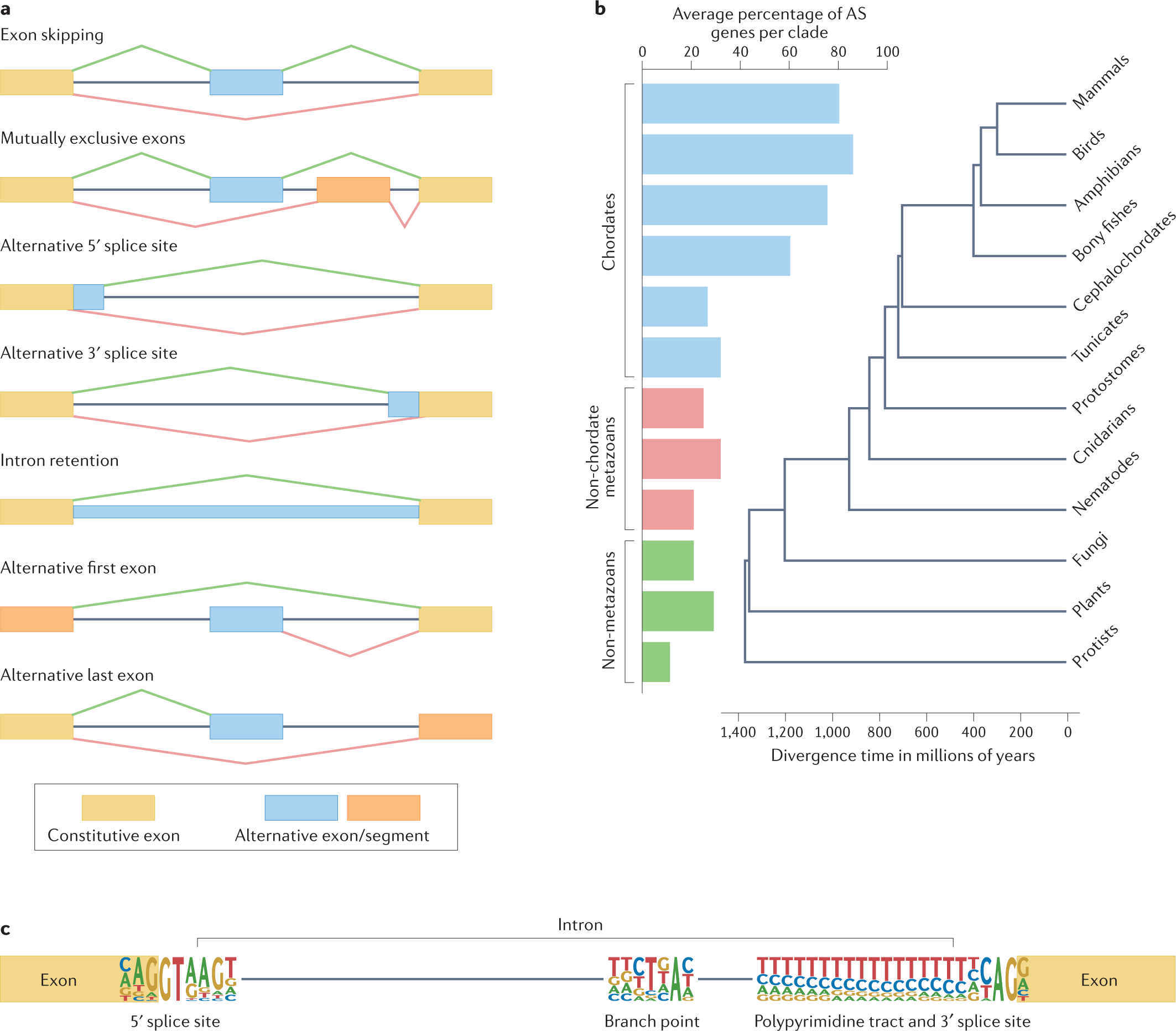
Alternative Splicing Regulatory Networks: Functions, Mechanisms

Splicing repression allows the gradual emergence of new Alu-exons in primate evolution. - Abstract - Europe PMC
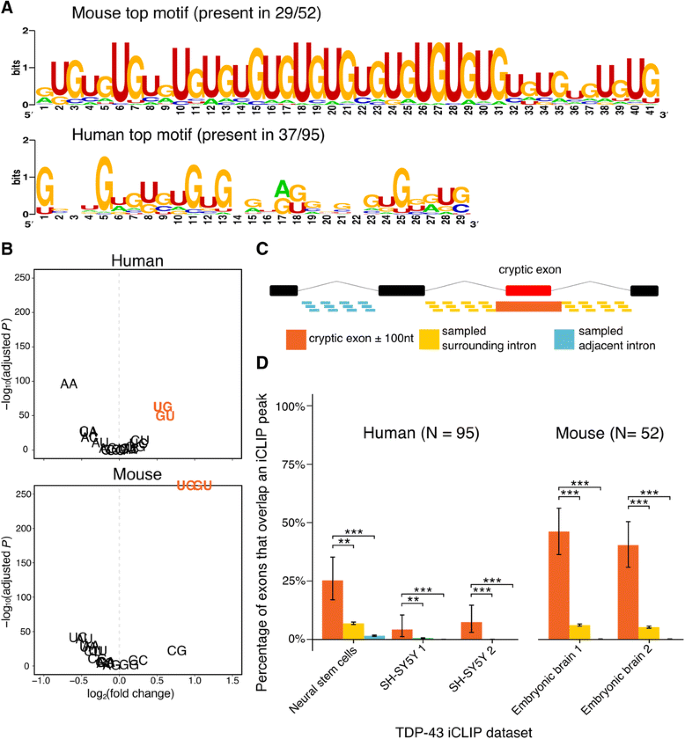
Quantitative analysis of cryptic splicing associated with TDP-43

LINE-1 elements contain multiple splice sites. ( A ) A schematic
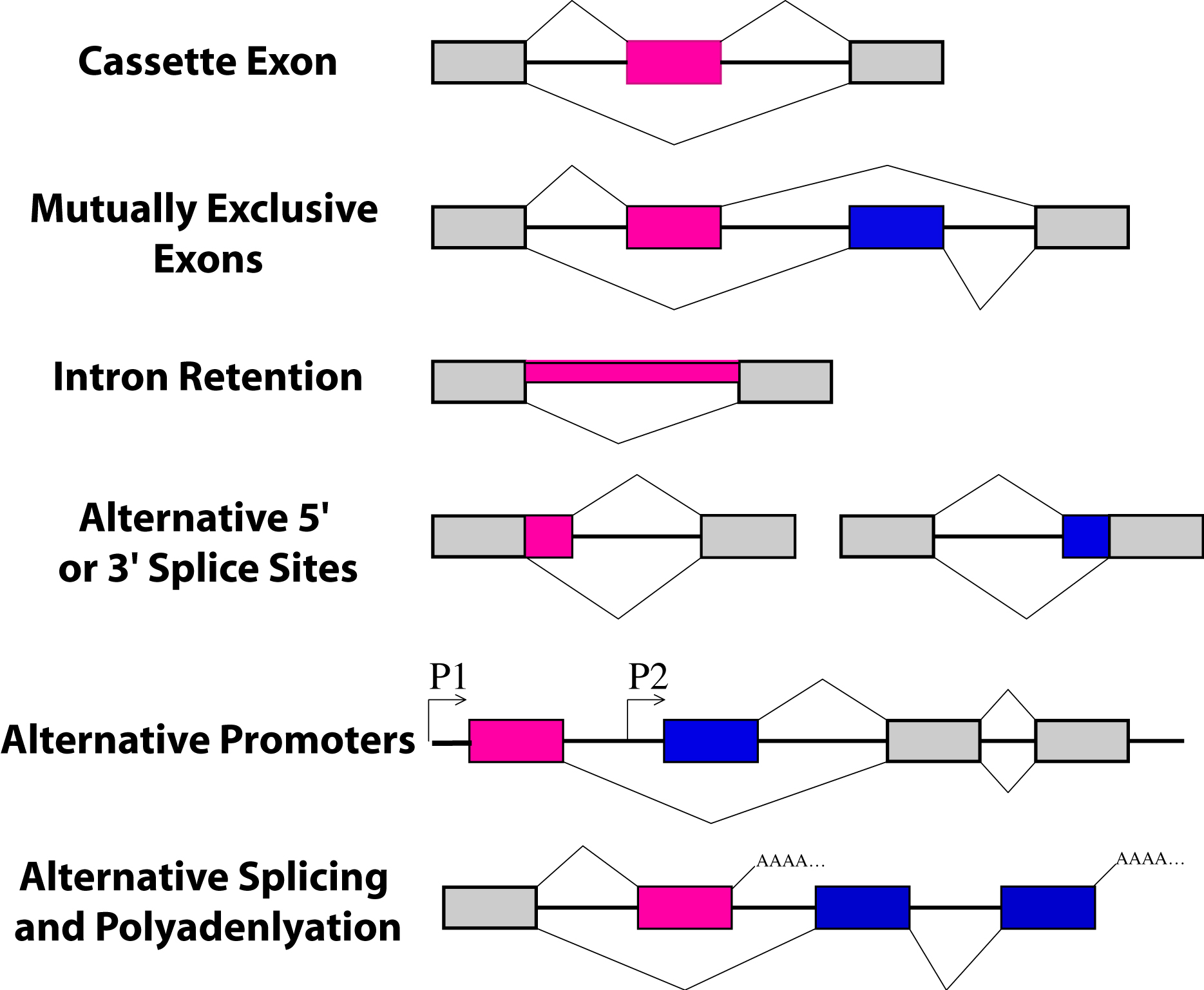
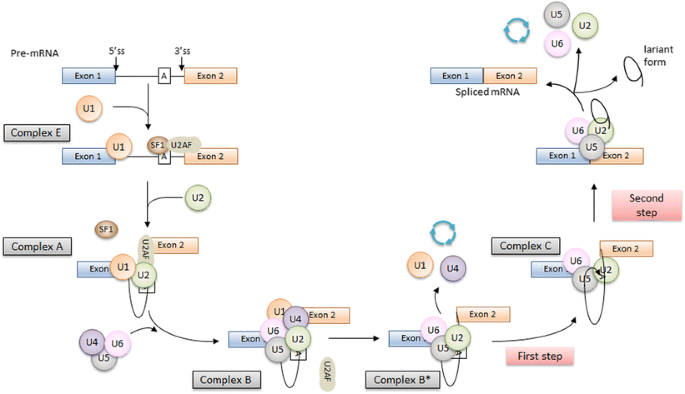
Pre-mRNA splicing and its regulation in Caenorhabditis elegans

Alu-exon age correlates with loss of U-tracts and repression by hnRNPC.

Roles and mechanisms of alternative splicing in cancer







