Physical mechanisms explaining DNA and RNA twist changes
4.6 (489) · $ 8.00 · In stock

The double-helix structure of DNA is deformed by environmental stimuli, which will then affect gene expression, and eventually trigger a sequence of cellular processes. Recent research led by a physicist from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) observed substantial DNA deformations by ions and temperature changes. The researchers developed one simple physical model to explain DNA deformations. These results provide new insights into the molecular mechanisms of cellular responses to ions and temperature changes and can be used to control gene expression using ions and temperature.
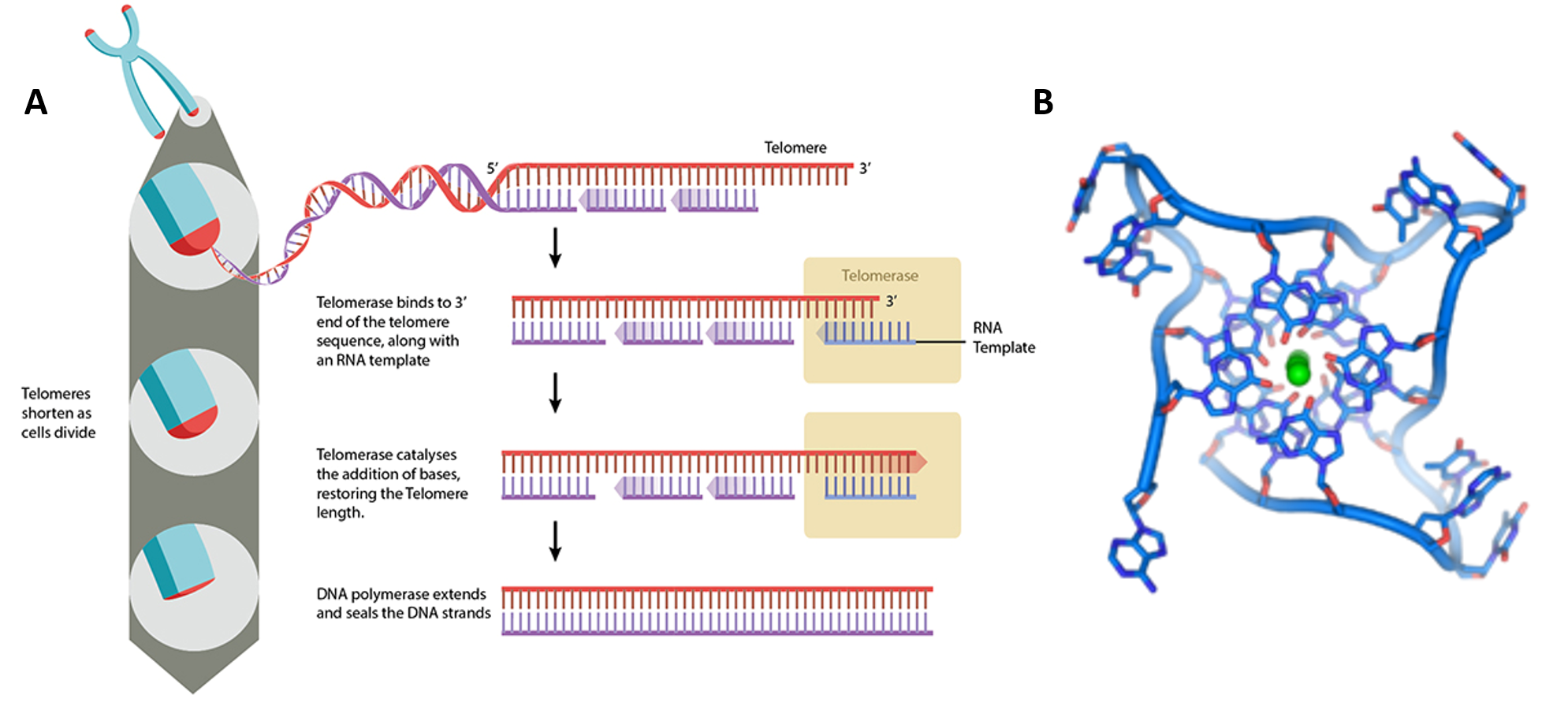
Chapter 4: DNA, RNA, and the Human Genome - Chemistry
» Nuus Hooftrekke van Suid-Afrika en die Wêreld
» Nuus Hooftrekke van Suid-Afrika en die Wêreld
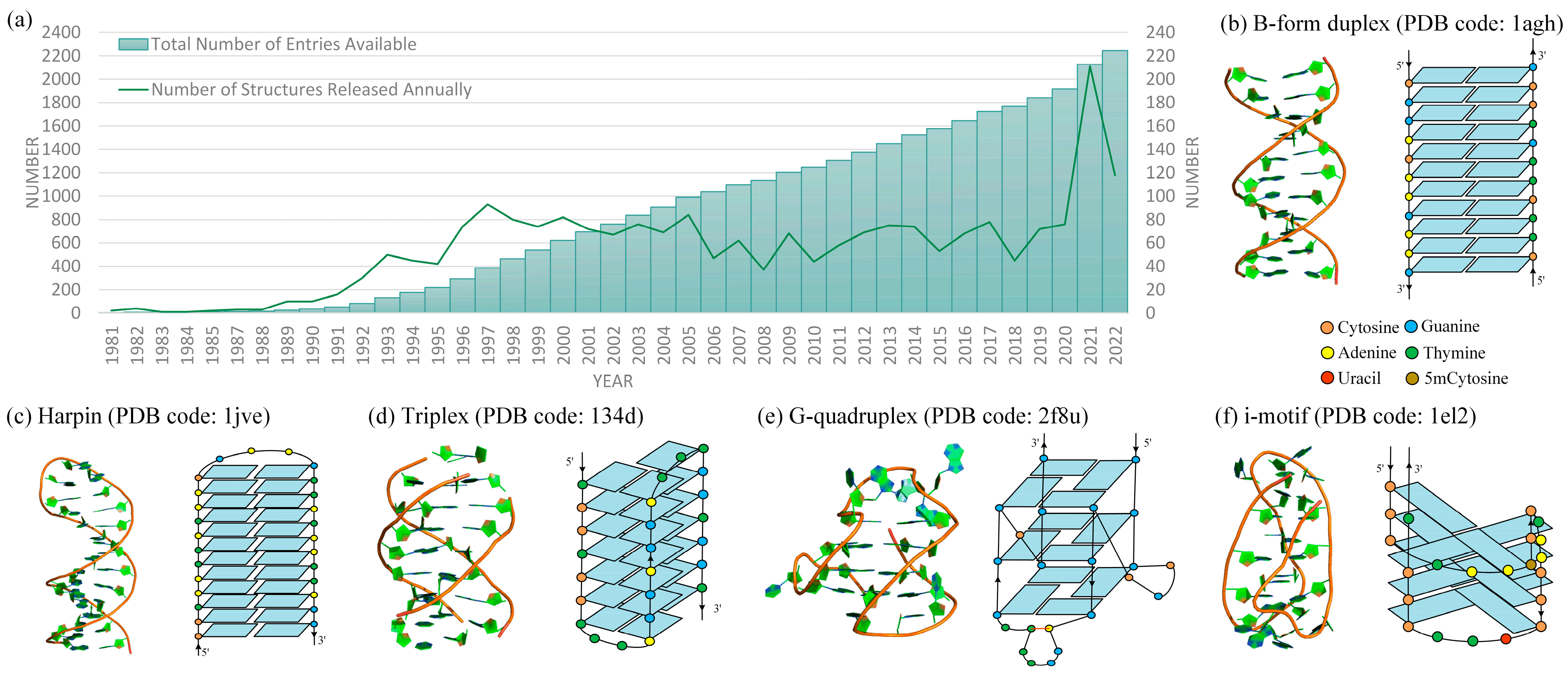
Molecules, Free Full-Text

» Nuus Hooftrekke van Suid-Afrika en die Wêreld

Mechanism of reaction of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from SARS
Publications, Department of Physics

DNA Supercoiling: an Ancestral Regulator of Gene Expression in

» Nuus Hooftrekke van Suid-Afrika en die Wêreld

Nucleoid - Wikipedia
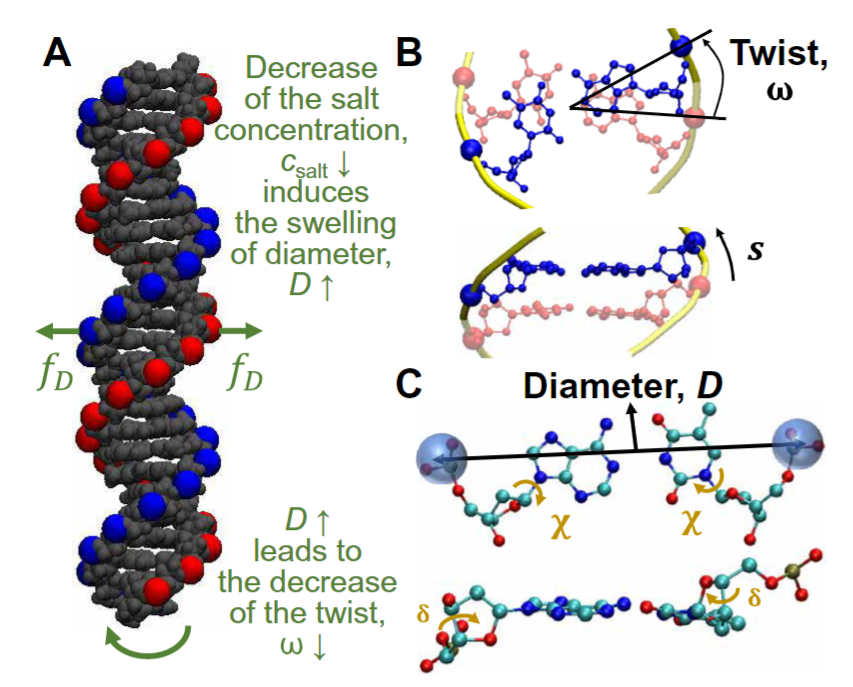
Publications, Department of Physics

PDF) On the common pathways of deformation: RNA vs DNA under

Mechanisms of transcriptional regulation by DNA supercoiling. (A







