Upper back pain in postmenopausal women and associated physical characteristics
4.8 (153) · $ 19.99 · In stock
The physical characteristics of postmenopausal women that are associated with upper back pain are not well-understood. The aim of this cross-sectional study was to identify the physical characteristics associated with presence and severity of upper back pain in healthy postmenopausal women. Self-reported upper back pain presence (within the previous month) and severity (numerical rating scale) were examined against the physical characteristics: height; weight; body mass index; breast size; breast ptosis; upper back extensor muscle endurance (isometric chest raise test); head, shoulder and upper back posture (photogrammetry); thoracic extension mobility (photogrammetry); bone mineral density (dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA)); body composition (DXA); and thoracic kyphosis, thoracic osteoarthritis and thoracic vertebral fracture (all radiography). A multivariable logistic regression model, adjusted for age, was built using physical characteristics with a significant univariate association with upper back pain. Censored Tobit regression, adjusted for age, was used to examine each physical characteristic against upper back pain severity. Postmenopausal women (n = 119) with a mean (SD) age of 61.4 (7.0) years participated in the study. After adjusting for age, the physical characteristics independently associated with upper back pain were: height (OR: 0.50, 95% CI: 0.31–0.79); and upper back extensor muscle endurance (OR: 0.46, 95%CI: 0.28–0.75). This model explained 31% of the variance in upper back pain (p<0.001). After adjusting for age, being taller and having better upper back extensor muscle endurance were associated with lower odds for upper back pain. After adjusting for age, differences in upper back pain severity were explained by upper back extensor muscle endurance (p = <0.001) and lean mass (p = 0.01). Conclusion: As a modifiable physical characteristic of postmenopausal women with upper back pain, upper back extensor muscle endurance is worth considering clinically.

Hormonal and reproductive factors are associated with chronic low back pain and chronic upper extremity pain in women--the MORGEN study.

images./img/2022/09/17/550x309/b

PDF) Efficacy of a multimodal physiotherapy treatment program for postural disorders and pain: a case report

The Link Between Menopause and Joint Pain
.jpg)
Cushing's Syndrome Signs and Symptoms
-min.jpg)
How to relieve Back Pain Conditions in Women

Surprising Menopause Symptoms

The Clinical Relevance of Hyperkyphosis: A Narrative Review

Breast size score conversion chart.
Upper back pain in postmenopausal women and associated physical characteristics

5 surprising ways menopause causes musculoskeletal symptoms - Core Clinics

Understanding Upper Left Side Back Pain: Causes & Remedies
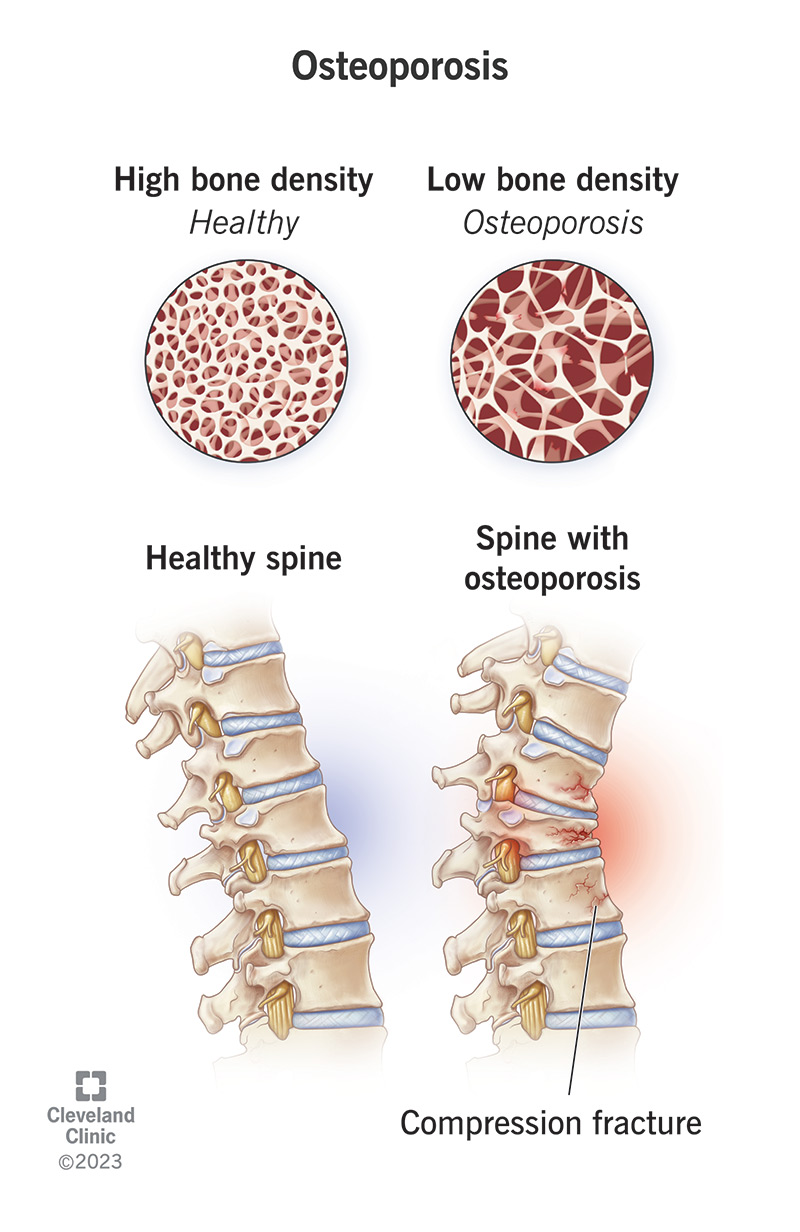
Osteoporosis: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment

Linda SPENCER, Senior Physiotherapist, Doctor of Philosophy, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Department of Physiotherapy