SARS-CoV-2 spike protein promotes inflammatory cytokine activation and aggravates rheumatoid arthritis, Cell Communication and Signaling
5 (583) · $ 23.99 · In stock
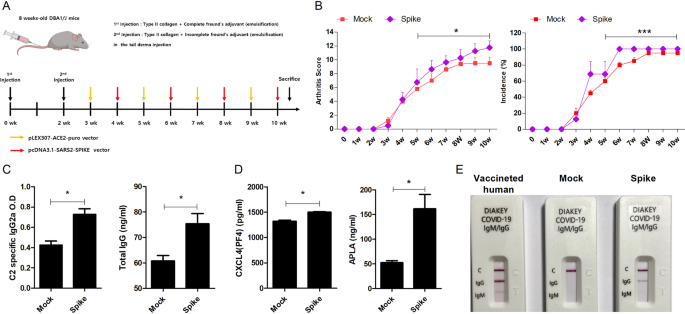
Background Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) induces inflammation, autoantibody production, and thrombosis, which are common symptoms of autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, the effect of COVID-19 on autoimmune disease is not yet fully understood. Methods This study was performed to investigate the effects of COVID-19 on the development and progression of RA using a collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) animal model. Human fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) were transduced with lentivirus carrying the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein gene in vitro, and the levels of inflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression were measured. For in vivo experiments, CIA mice were injected with the gene encoding SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, and disease severity, levels of autoantibodies, thrombotic factors, and inflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression were assessed. In the in vitro experiments, the levels of inflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression were significantly increased by overexpression of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in human FLS. Results The incidence and severity of RA in CIA mice were slightly increased by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in vivo. In addition, the levels of autoantibodies and thrombotic factors, such as anti-CXC chemokine ligand 4 (CXCL4, also called PF4) antibodies and anti-phospholipid antibodies were significantly increased by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Furthermore, tissue destruction and inflammatory cytokine level in joint tissue were markedly increased in CIA mice by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Conclusions The results of the present study suggested that COVID-19 accelerates the development and progression of RA by increasing inflammation, autoantibody production, and thrombosis. Video Abstract
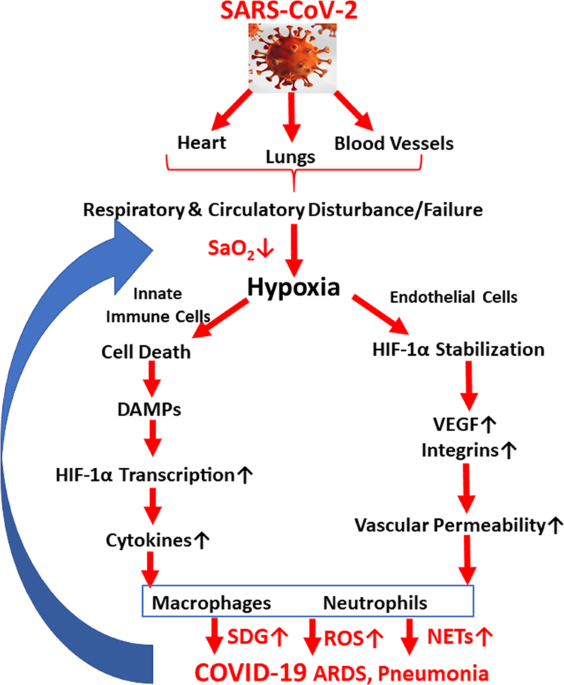
Hypoxia, HIF-1α, and COVID-19: from pathogenic factors to potential therapeutic targets
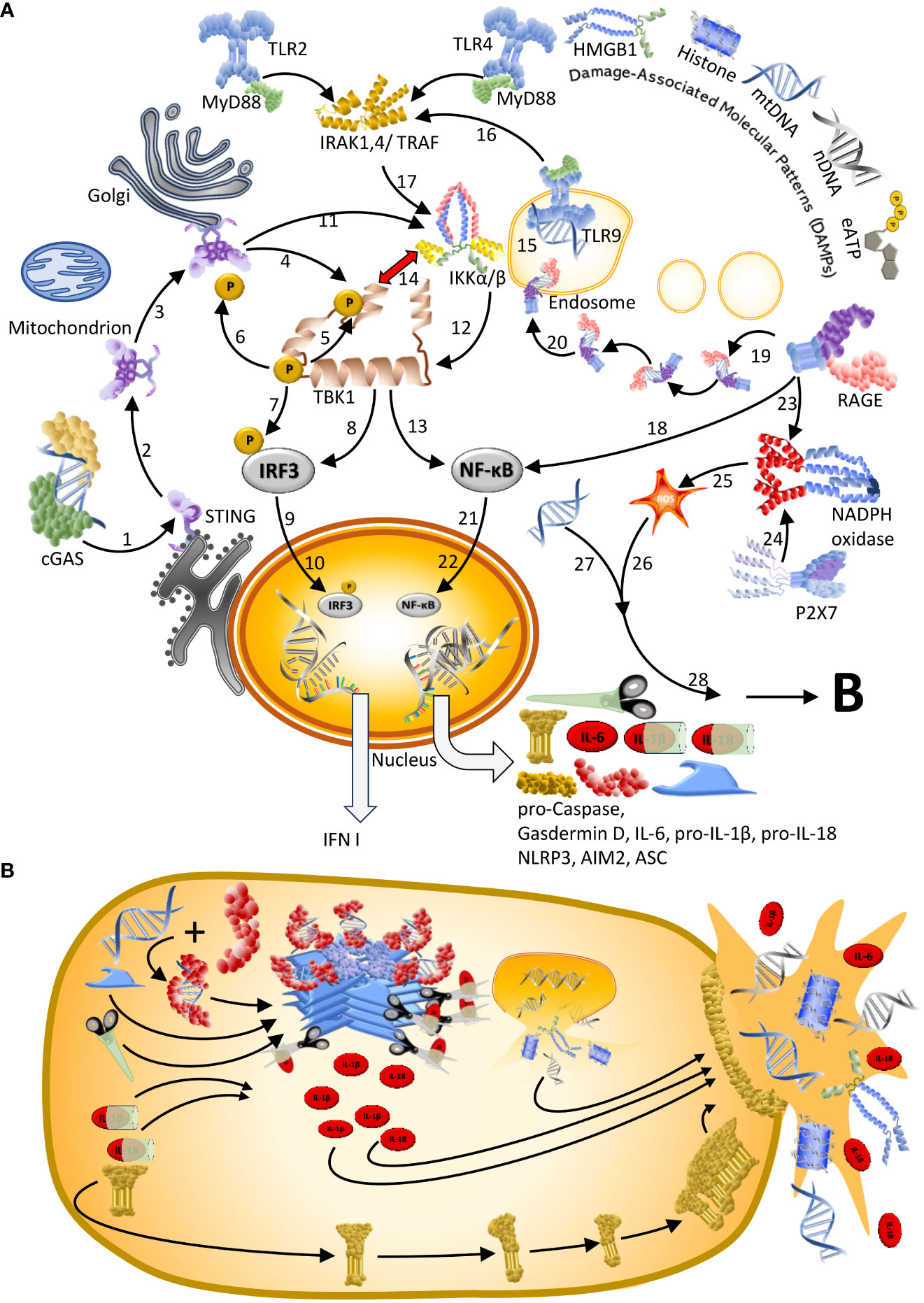
Frontiers Self-DNA driven inflammation in COVID-19 and after mRNA-based vaccination: lessons for non-COVID-19 pathologies
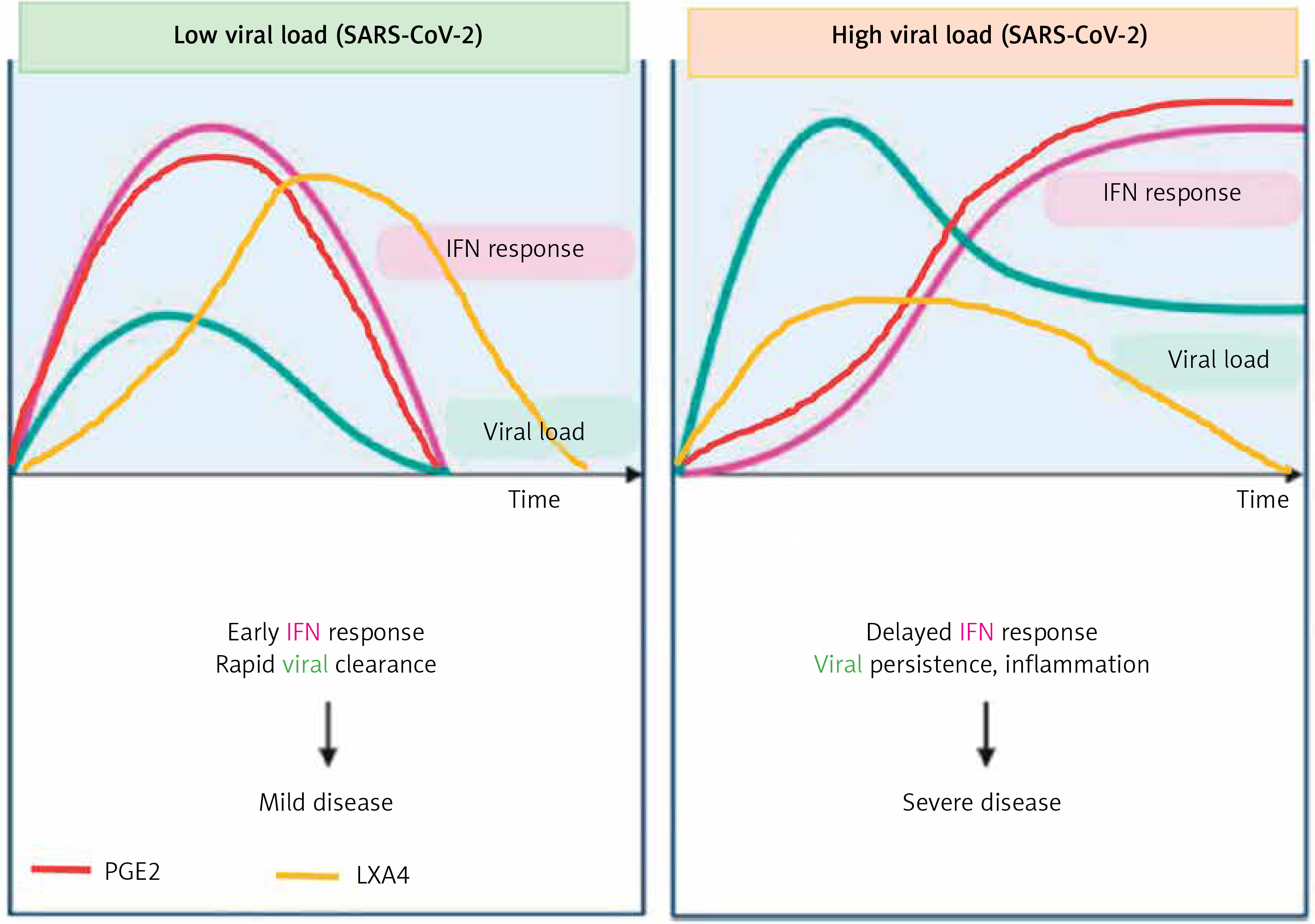
Bioactive lipid-based therapeutic approach to COVID-19 and other similar infections

Inflammation Triggered by SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2 Augment Drives Multiple Organ Failure of Severe COVID-19: Molecular Mechanisms and Implications

Functional foods as immunomodulators: Tackling the SARS-CoV-2 related cytokine storm–A review - ScienceDirect
PDF) SARS-CoV-2 spike protein promotes inflammatory cytokine activation and aggravates rheumatoid arthritis
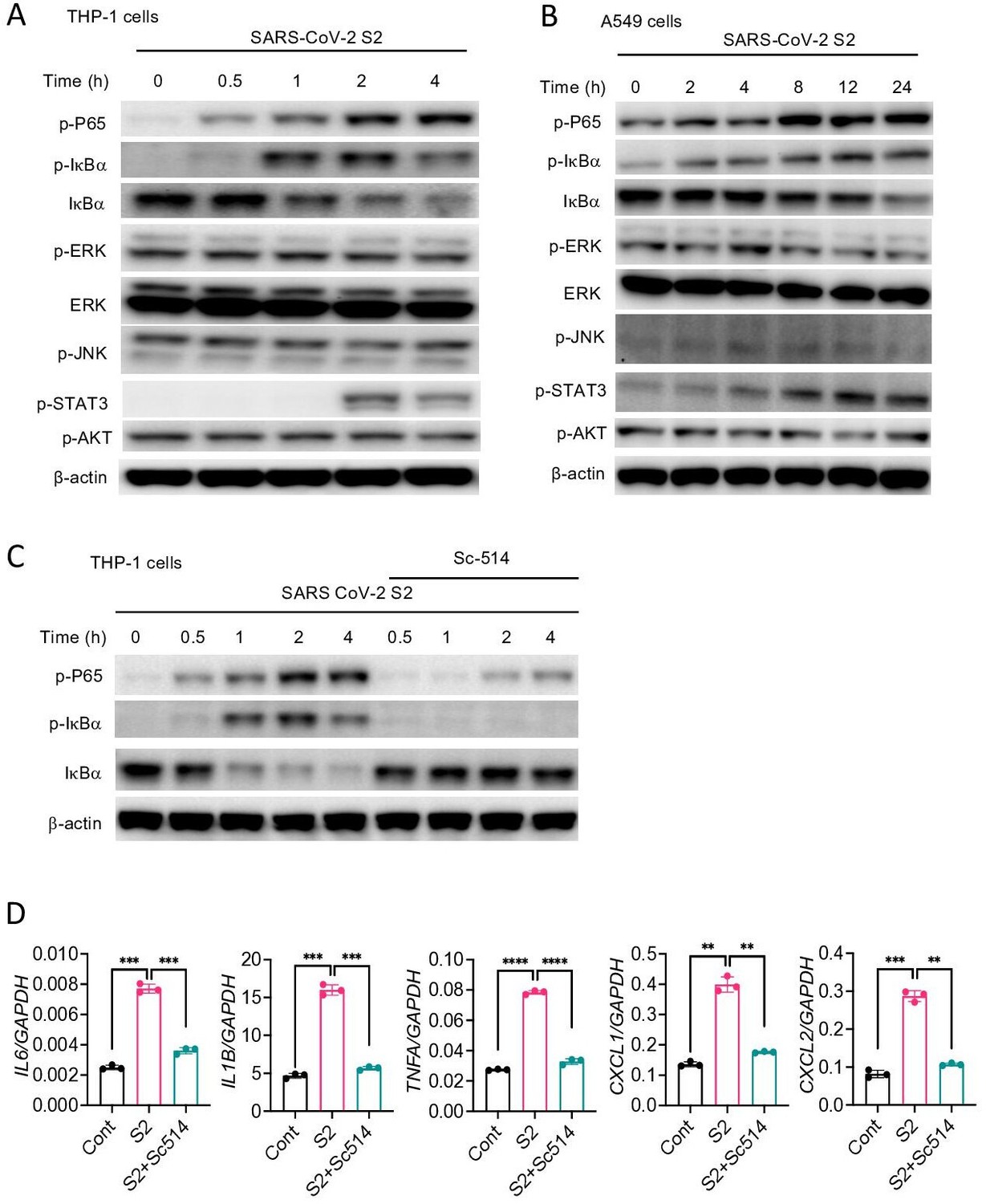
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces inflammation via TLR2-dependent activation of the NF-κB pathway

Systematic functional analysis of SARS-CoV-2 proteins uncovers viral innate immune antagonists and remaining vulnerabilities - ScienceDirect
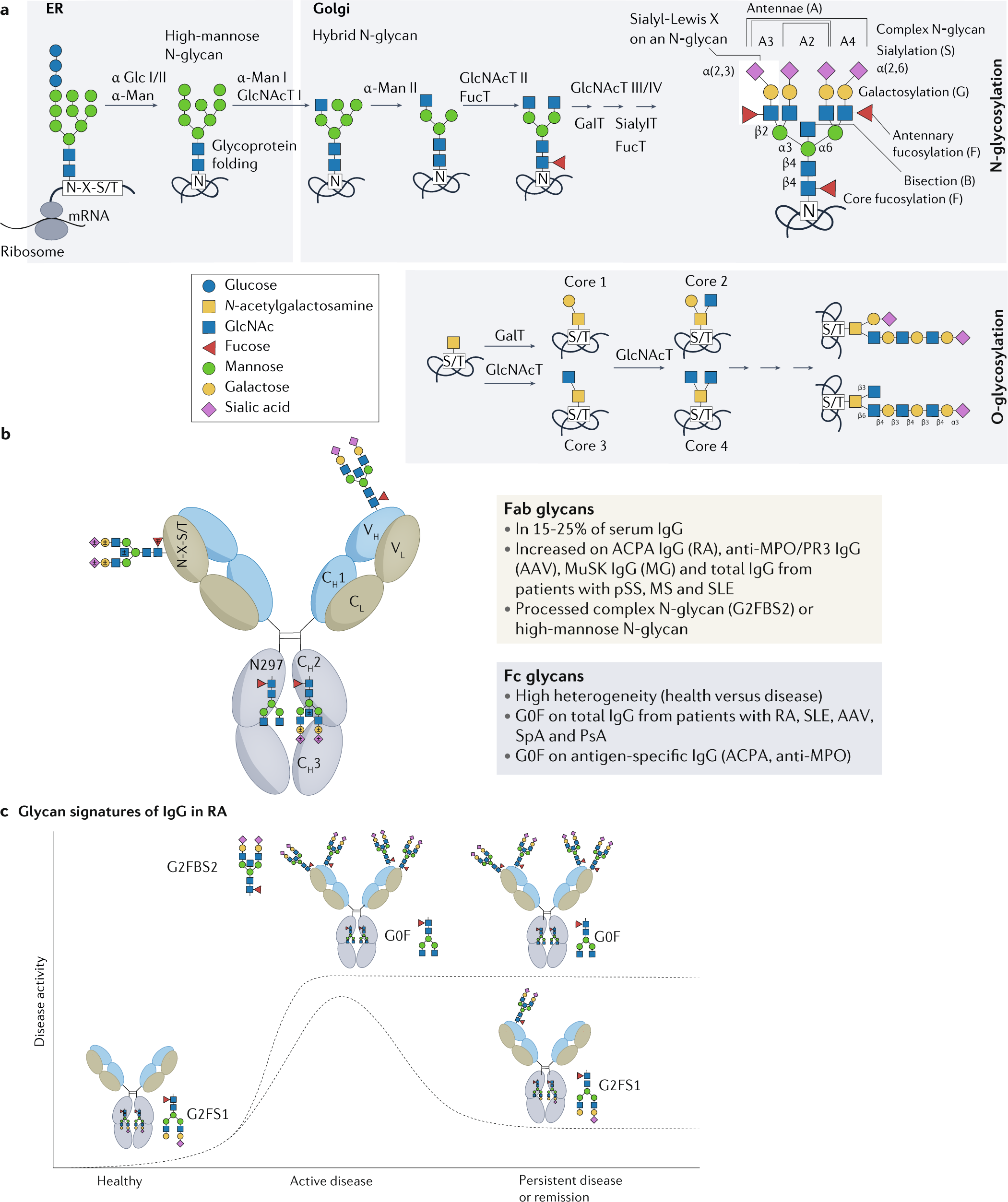
Glycobiology of rheumatic diseases

FOXP3 Antibody PE 12-5773-82 from Thermo Fisher Scientific
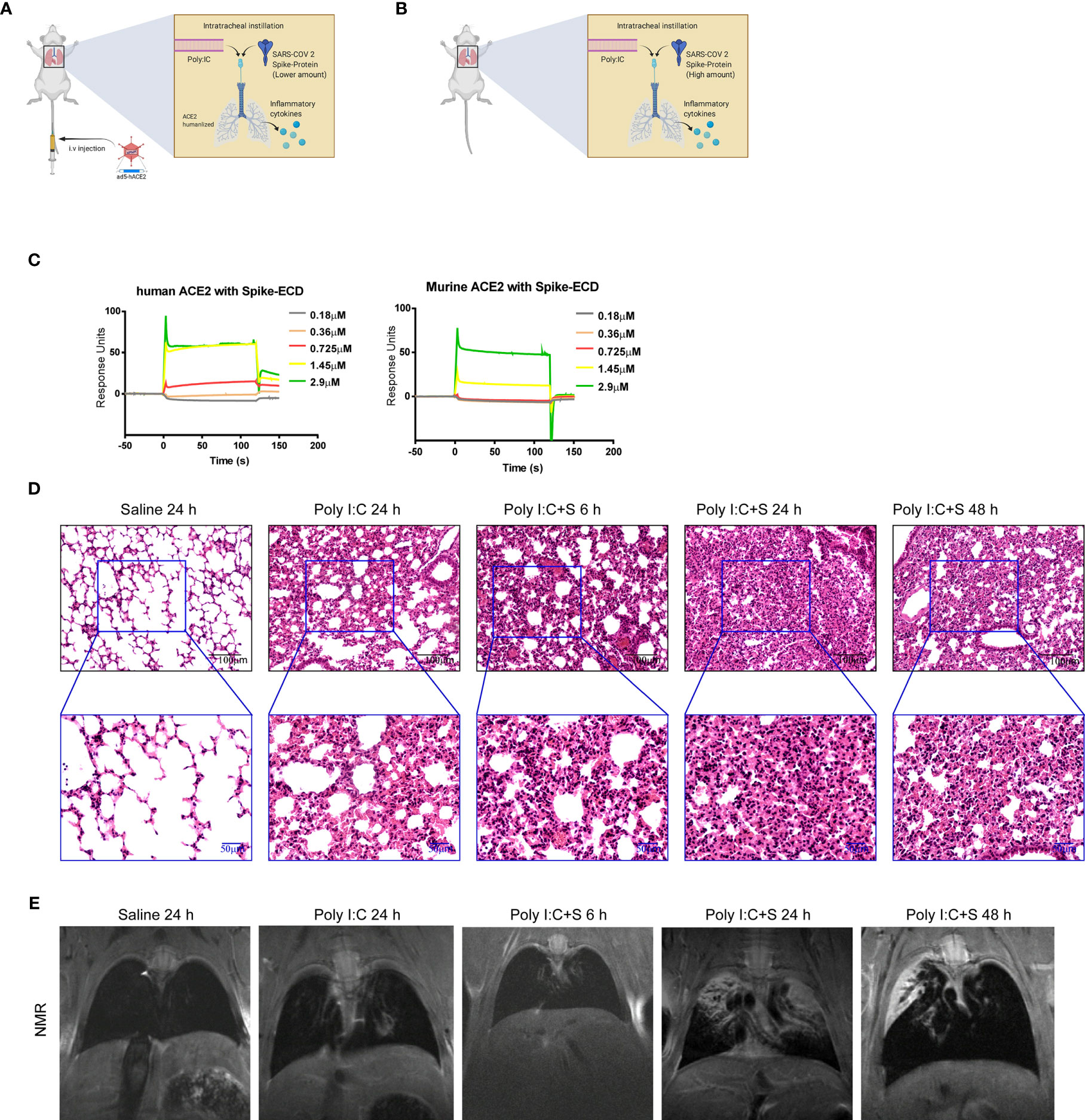
Frontiers Cytokine Signature Induced by SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein in a Mouse Model
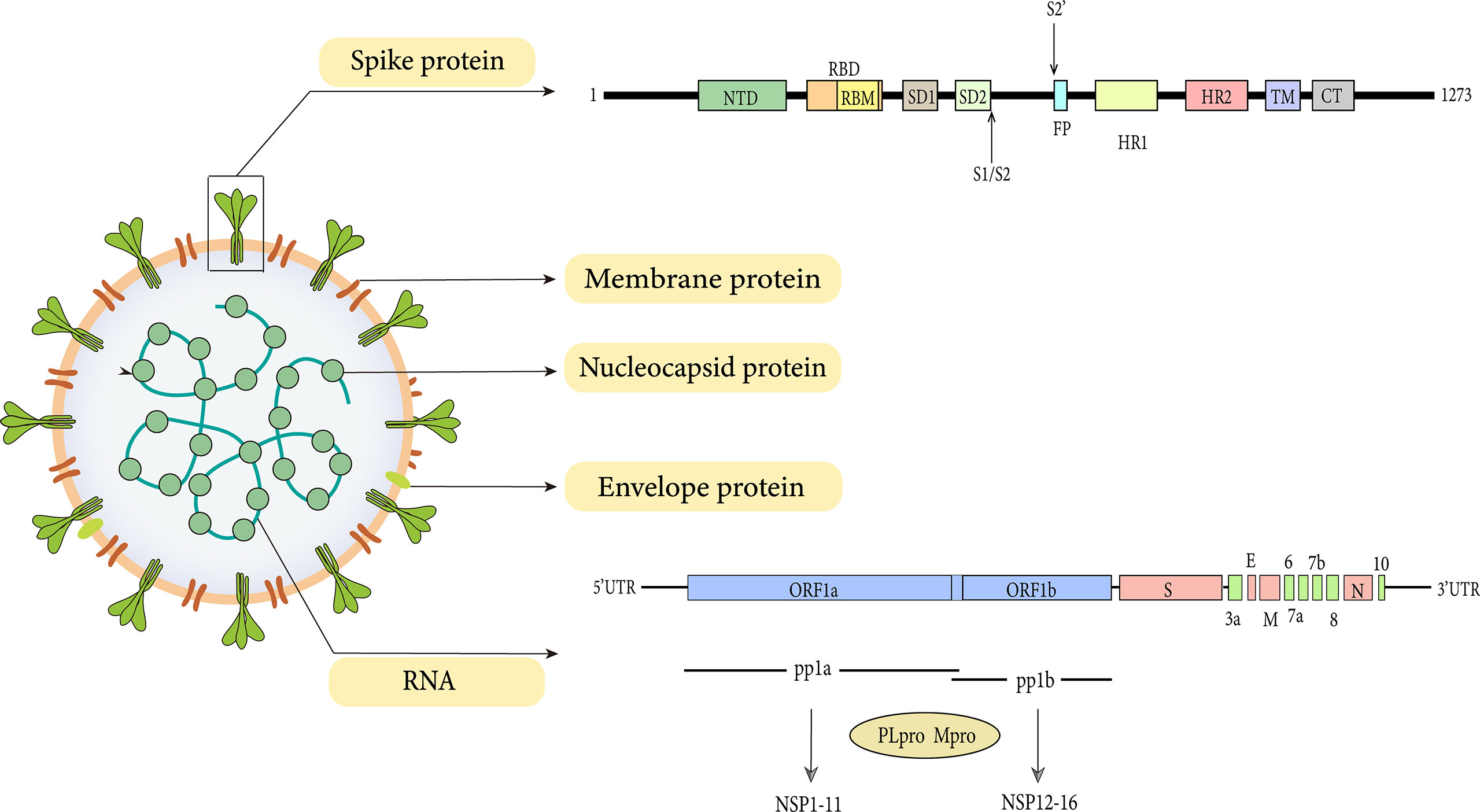
Frontiers SARS-CoV-2 and Emerging Variants: Unmasking Structure, Function, Infection, and Immune Escape Mechanisms
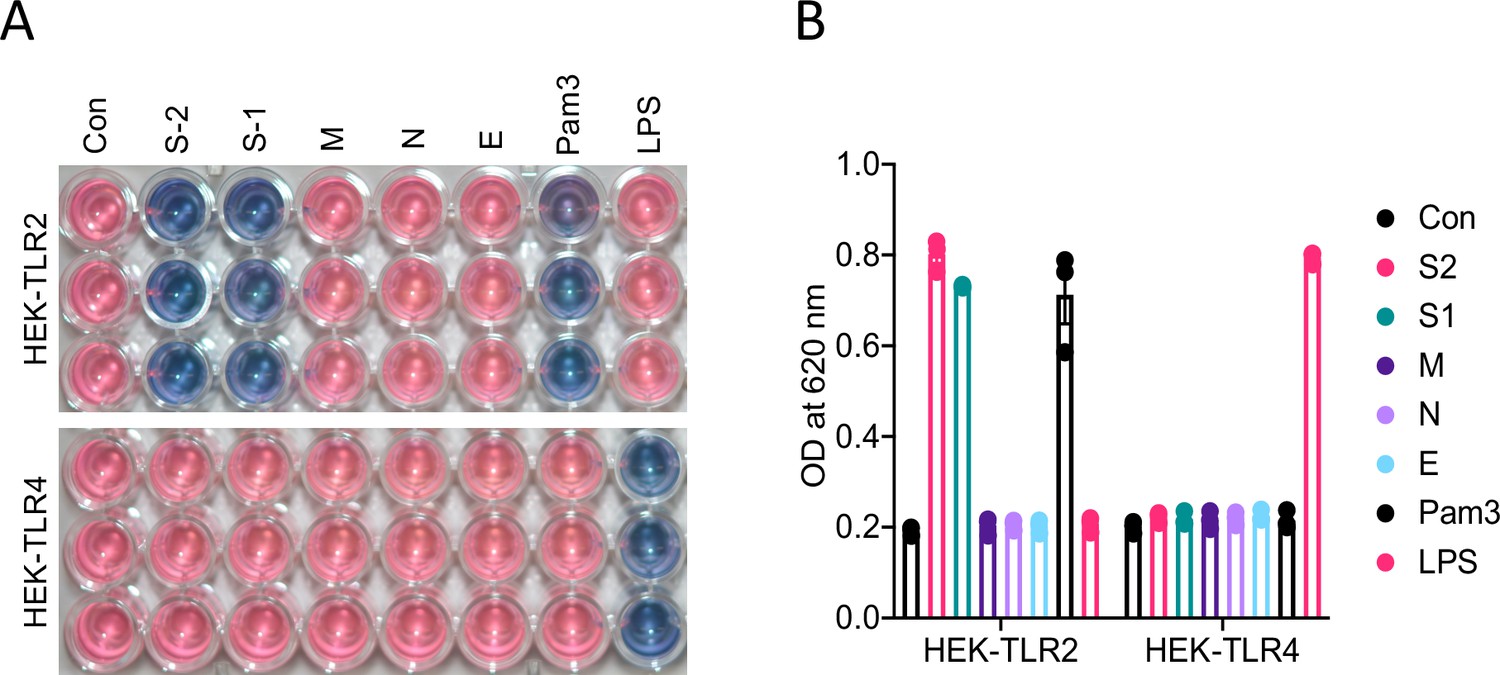
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces inflammation via TLR2-dependent activation of the NF-κB pathway





![What Does it Mean to Be a Spike in Magic? [6 Characteristics] - Draftsim](https://draftsim.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Spike-Tournament-Grinder-Illustration-by-Zoltan-Boros.png)