Hyperpolarization of membrane potential reveals prominent spikelets at
4.9 (792) · $ 9.99 · In stock

Changes in MT membrane potential result in reduced dendritic Ca 2
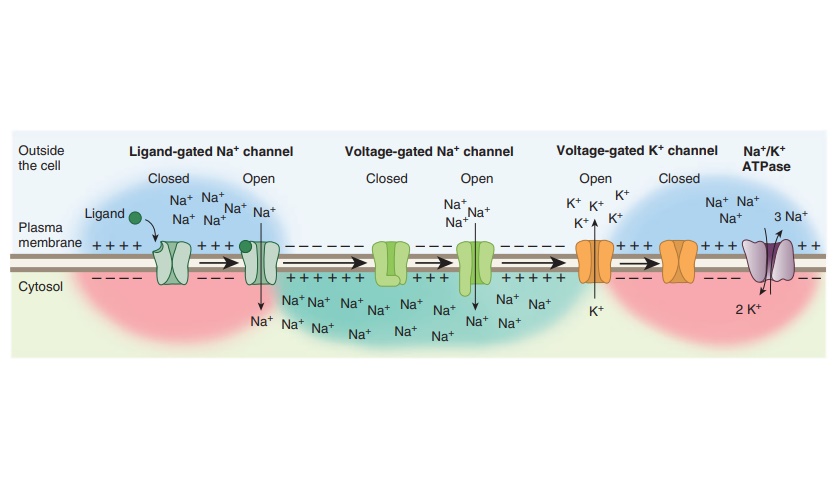
Cell Membrane Potential

SPW-R-coupled action potentials are antidromic spikes. (A Upper) Action
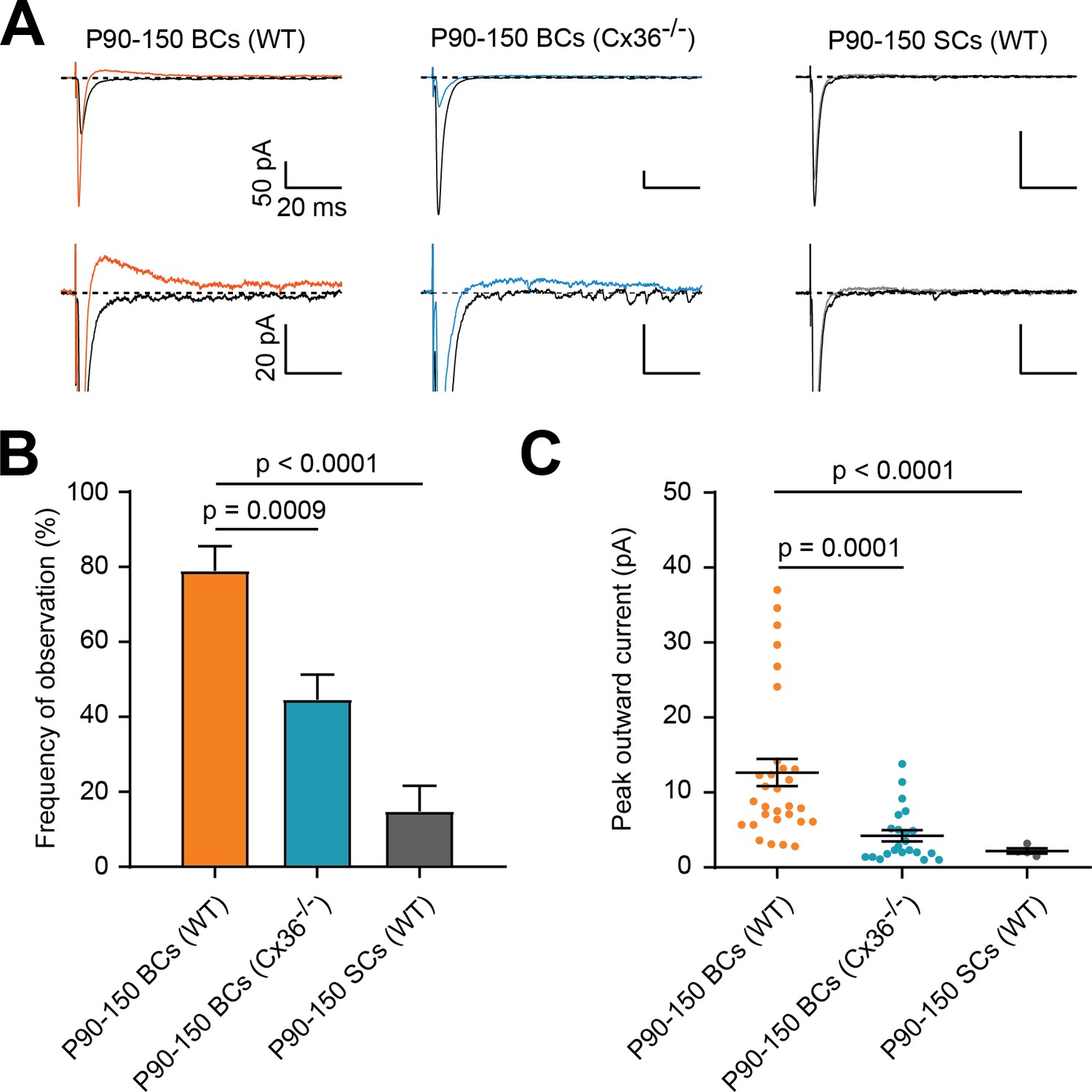
Feed-forward recruitment of electrical synapses enhances synchronous spiking in the mouse cerebellar cortex

Chapter 3b - Properties of Excitable Membranes: Spikes

Qian SUN, Assistant Professor, PhD, Case Western Reserve University, Ohio, CWRU, Department of Neurosciences
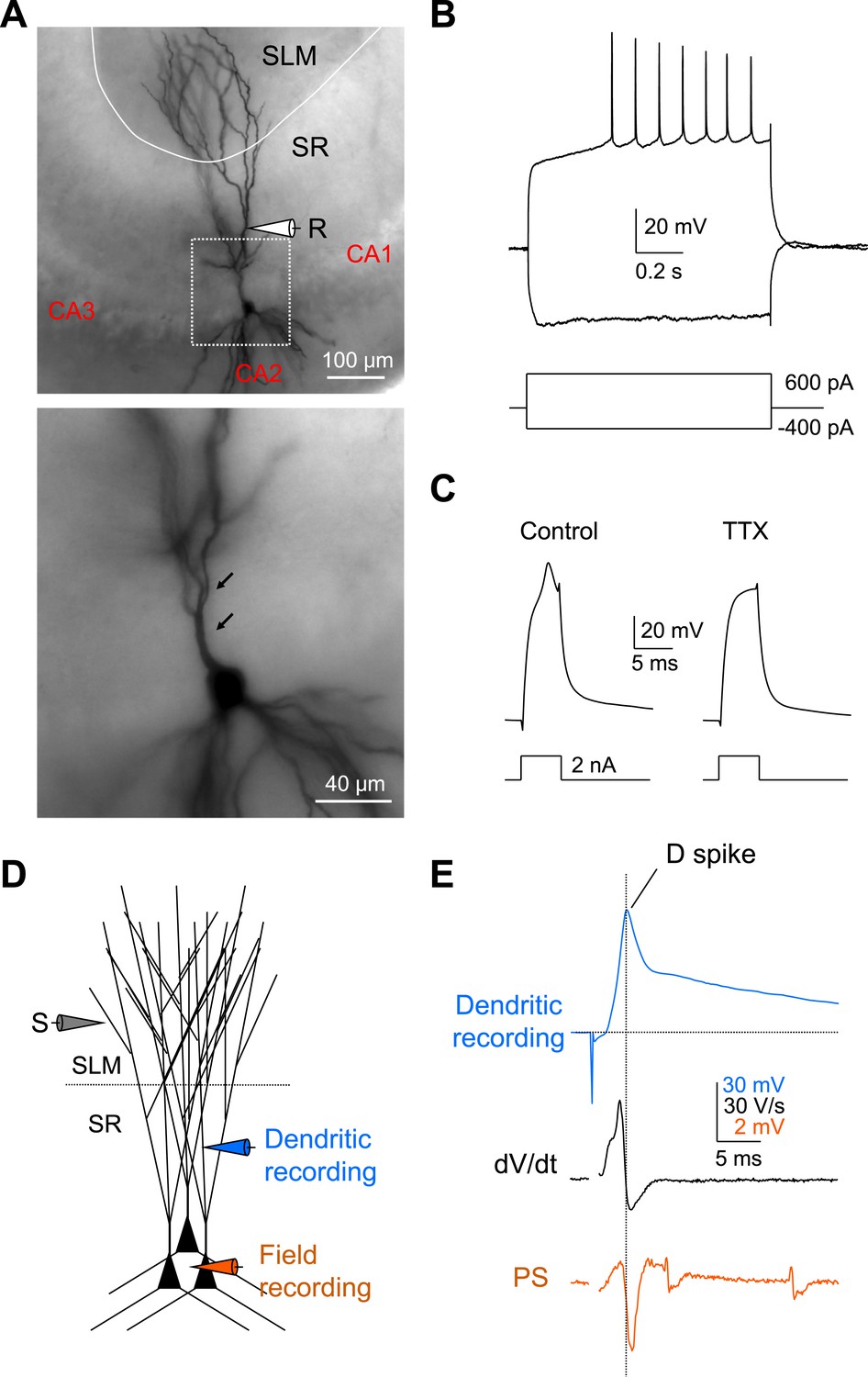
Dendritic Na+ spikes enable cortical input to drive action potential output from hippocampal CA2 pyramidal neurons

Local glutamate-mediated dendritic plateau potentials change the state of the cortical pyramidal neuron
The relationship between axial current loss (dendritic load) and

Theta oscillations coincide with sustained hyperpolarization in CA3 pyramidal cells, underlying decreased firing
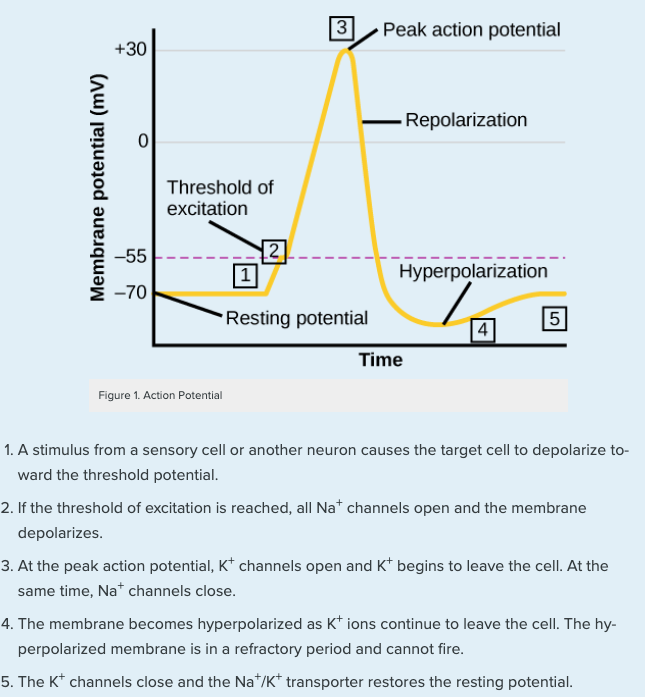
Action Potentials – Human Physiology

Hyperpolarization of membrane potential reveals prominent spikelets at

Adrenergic Modulation Regulates the Dendritic Excitability of Layer 5 Pyramidal Neurons In Vivo - ScienceDirect
The relationship between axial current loss (dendritic load) and

Chapter 3b - Properties of Excitable Membranes: Spikes







