A powered simple walking model explains the decline in propulsive force and hip flexion torque compensation in human gait
4.5 (306) · $ 18.99 · In stock


SLR speeds for walking and running for both experiments. Data points

教員紹介

The Age-Associated Reduction in Propulsive Power Generation in Walking

Preferred walking speed selected by older and young participants during

PDF) A powered simple walking model explains the decline in

Researcher Directory - Osaka University

教員紹介

Investigation of the relationship between steps required to stop and propulsive force using simple walking models - ScienceDirect
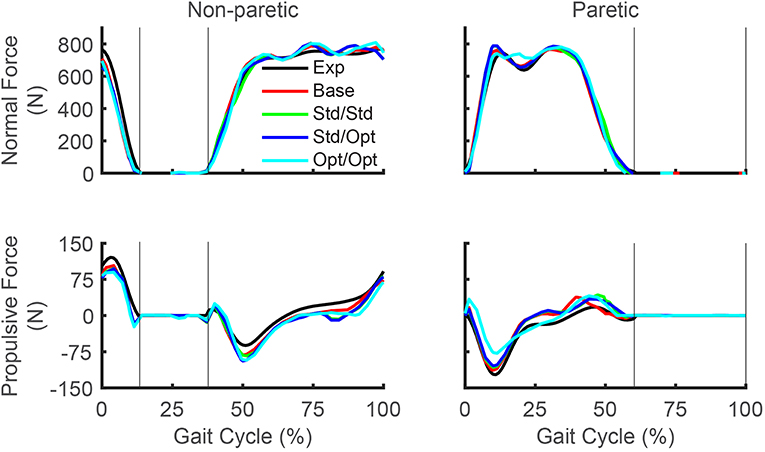
Frontiers Computational Design of FastFES Treatment to Improve Propulsive Force Symmetry During Post-stroke Gait: A Feasibility Study

The CoM trajectory of a periodic motion, and its projections in
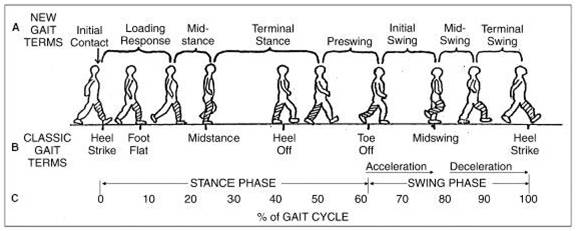
Gait - Physiopedia

教員紹介







